Choose Your State of Service
In order to serve you better, please select your Dominion Energy location services.
In order to serve you better, please select your Dominion Energy location services.
In order to serve you better, please select your Dominion Energy location services.
Always prepared, always committed to safety in our community.
This page contains emergency preparedness information for those living or visiting within approximately 10 miles of Dominion Energy’s nuclear power plants (or referred to as emergency planning zones or EPZs). The following information is provided for educational purposes on how to prepare in the unlikely event of an emergency at one of our nuclear power stations.
This information is updated on a regular basis. Select the nuclear power station closest to you for emergency preparedness information specific to that station:
Radiation is energy emitted in tiny waves or particles. It naturally occurs in the environment; it is not new or mysterious. We receive radiation from the sun, minerals in the earth, food we eat, and building materials. We even give off radiation.
You can’t see, taste, or hear radiation. However, you can measure radiation – in units called rem and millirem. The rem is a unit of measure that considers the effect that different types of radiation have on the body.
The table below shows the average mrem an individual in the United States receives from naturally occurring and man-made radioactive material.
|
Natural Background |
|
|
Radon and Radon Daughters |
228.0 mrem |
|
Cosmic Rays |
33.0 mrem |
|
Terrestrial Radiation |
21.0 mrem |
|
Internal Radiation |
29.0 mrem |
|
Per Year Total: |
311.0 mrem |
|
Man-Made |
|
|
Diagnostic X-Rays |
33.0 mrem |
|
Other Medical |
267.0 mrem |
|
Consumer Products |
13.0 mrem |
|
Occupational |
0.5 mrem |
|
Nuclear Power |
0.1 mrem |
|
Miscellaneous |
0.3 mrem |
|
Per Year Total: |
314.0 mrem |
Total Natural and Man-Made sources Per Year Total: 625.0 mrem
Radiation can produce charged particles in material it strikes. Charged particles are known as ions. The most common types of ionizing radiation are alpha, beta, and gamma:
Exposure to large amounts of radiation can be harmful or even fatal; however, radiation emitted during normal nuclear power plant operations is very small, smaller than the amount we would receive on a coast-to-coast airplane flight.
Radiation risk depends on:
Learn more about radiation and the various sources of radiation.
Nuclear plants produce electricity by boiling water to create steam, which turns a turbine to produce electricity. The difference is nuclear power plants create heat needed to boil water through nuclear fission. Nuclear fission is the physical process of splitting an atom to produce carbon-free electricity. Within the nuclear reactor, uranium, the most common nuclear fuel, is contained in small, ceramic pellets and placed in long, vertical tubes (called fuel rods). Fuel rods are then bundled together in fuel assemblies.
The animated graphic below shows how a pressurized water reactor works. The core inside in the Reactor Vessel creates heat (where nuclear fission takes place). The Pressurizer keeps water under high pressure so that it heats but does not boil. The Steam Generator converts water coming from the reactor core into steam. Water from the reactor and the water in the steam generator that is turned into steam never mix. This allows most radioactivity to stay in the reactor area. Steam is then pumped into a Turbine, pushing giant blades to turn the electrical Generator. Electricity is produced and transmitted to your home. After turning the turbines, unused steam is cooled and condensed by cooling water from a water source through the Condenser. The condensed steam – now water – is pumped back into the Steam Generator to be reheated and the process is repeated.
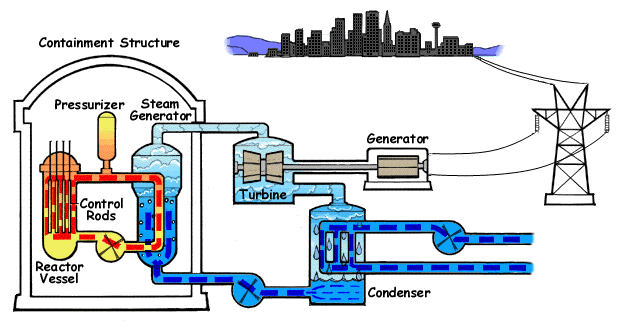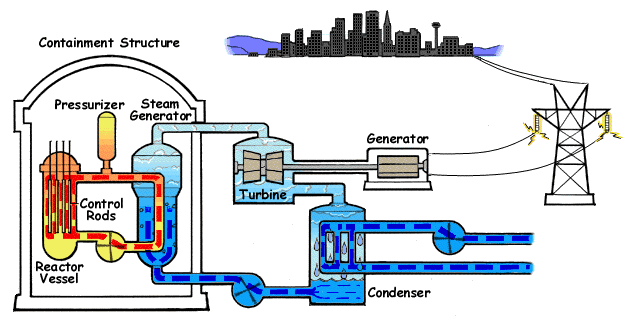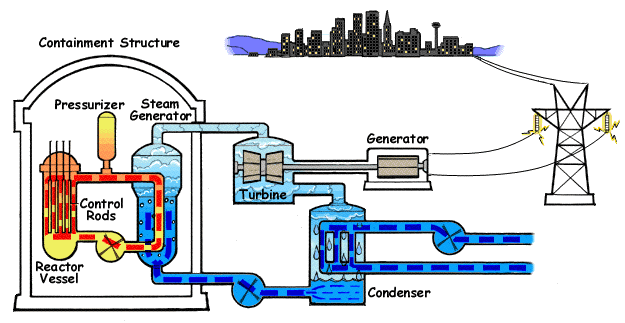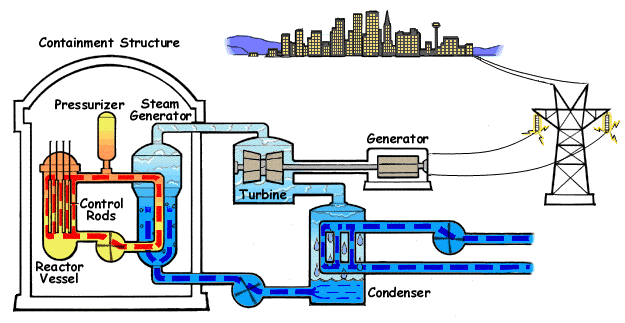
Nuclear power stations are designed and built to prevent large amounts of radioactivity from reaching the environment, both during normal operation and in the event of an accident. These intensive efforts by the industry have worked well in the more than 40 years of nuclear power production in this country, without a single radiation-related death or serious injury involving a member of the public having ever been recorded. The likelihood of such an occurrence in the future is extremely small.
Copyright © 2024 Dominion Energy
